Scatter diagram
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
If you’ve ever struggled with visualizing data, you’re not alone. As a data enthusiast, I’ve often found myself frustrated with trying to convey my findings in a way that is both digestible and engaging. Luckily, I discovered the power of scatter plots to help simplify complex data sets into easily understandable visualizations.
Many data analysts struggle with the same issues when it comes to visualizing information. Their audiences often lose interest or get bogged down in complex details. Scatter plots offer a simple-to-understand solution. With only a few clicks, you can create a scatter plot that makes your data easy to recognize, access, and understand.
Drawing a scatter plot is straightforward. To begin, open a spreadsheet program such as Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets. Next, input the data points that you want to plot onto the scatter plot. This could mean values plotted by time, difference, or another measurable metric. Then, click on the Chart icon and select Scatter plot. You can now customize your scatter plot with different colors, shapes, and labels to help clarify the data points. Finally, make sure to choose an appropriate title that helps convey the central theme of your plot.
In conclusion, scatter plots offer a user-friendly way to visualize large data sets. By summarizing complex information into a centralized plot, you can express your findings in an easy-to-digest manner. Learning how to draw a scatter plot can help you unlock a deeper understanding of your data.
How to Draw a Scatter Plot
I once had to analyze data for a sales department and present the data to a group of stakeholders. The data showed the company’s performance over the last five years, and I was tasked with visualizing this data in a way that was easily digestible. I was able to quickly draw a scatter plot, which helped to simplify a complicated dataset into something that everyone could understand.
The first step in drawing a scatter plot is creating a spreadsheet and entering all your data points. Once your data is complete, select the chart icon from the menu ribbon, and select a scatter plot. After this, customize the scatter plot by changing the color, shape, and size of the points, so the plot is more visually appealing. Finally, label the axes, add a title, and legend to provide context for your scatter plot.
Why Draw a Scatter Plot?
Scatter plots are an effective way of visualizing two variables and identifying trends between these two variables. By plotting the data into a scatter plot, you can spot trends that are impossible to observe without visualizing data. For instance, a business owner can create a scatter plot of their sales and advertising expenses to observe how advertising affects sales. This data visualization will allow them to see if increased advertising translates into increased sales. As a result, scatter plots make it easy to understand complex datasets and provide insights into data trends.
Customizing Your Scatter Plot
When creating a scatter plot, you can use different point shapes, colors, and sizes to highlight different data sets. A best practice when creating a scatter plot is to use different shapes for different data sets, making differentiation simple. Colors can also be used to differentiate between data sets, or you can use different shades of a single color to represent different data groups.
Labeling Your Scatter Plot
Labeling your scatter plot is an essential step in communicating your findings. The title should summarize the central theme of your data. The x-axis and y-axis labels should define the two variables that are plotted. Finally, the legend should be used to help differentiate different data sets on the scatter plot.
FAQs about Scatter Plots ### Q: What is a scatter plot?
A: A scatter plot is a graph used to display values for two variables used in statistics that show how much one variable is affected by another. Each point on the scatter plot represents an observation in the data set.
Q: What does a scatter plot show?
A: A scatter plot shows a relationship between two variables where there are two axes –horizontal and vertical- showing a numeric value. Each point marks an observation, and the position of the point represents correlate to the values of the two variables.
Q: What is the purpose of a scatter plot?
A: Scatter plots are useful for visually examining the relationship between two variables. By creating a scatter plot, you can quickly find relationships, patterns, and trends in the data.
Q: Can a regression line be added to a scatter plot?
A: Yes. A regression line is often added to a scatter plot to help identify and quantify the strength of the relationship between two variables.
Conclusion of How to Draw a Scatter Plot
In summary, drawing a scatter plot is a powerful tool for displaying numerical data in a visual format. Scatter plots simplify and clarify complex data sets, making it easier to identify trends, patterns, and relationships. With a few steps, you can quickly create an attention-grabbing scatter plot that conveys your message effectively. Whether you are using scatter plots for tracking revenue, market research, or any other applications, they are a simple and valuable tool for data visualization.
Gallery
Matplotlib Scatter: Draw A Scatter Plot With Empty Circles Taking A
Photo Credit by: bing.com / scatter matplotlib plot draw circles empty distribution taking random w3resource output sample python
How Can I Draw Dot Plot (Column Scatter Graphs) For Different Groups

Photo Credit by: bing.com / dot scatter denote comparisons
Scatter Diagram
Photo Credit by: bing.com / scatter
Python - How To Draw Line Inside A Scatter Plot - Stack Overflow

Photo Credit by: bing.com / roc plot line scatter draw curve data python decision space wikipedia documentation examples inside curva matplotlib binary represent trend way
Scatter Plots And Trend Lines - Module 10.1 (Part 1) - YouTube
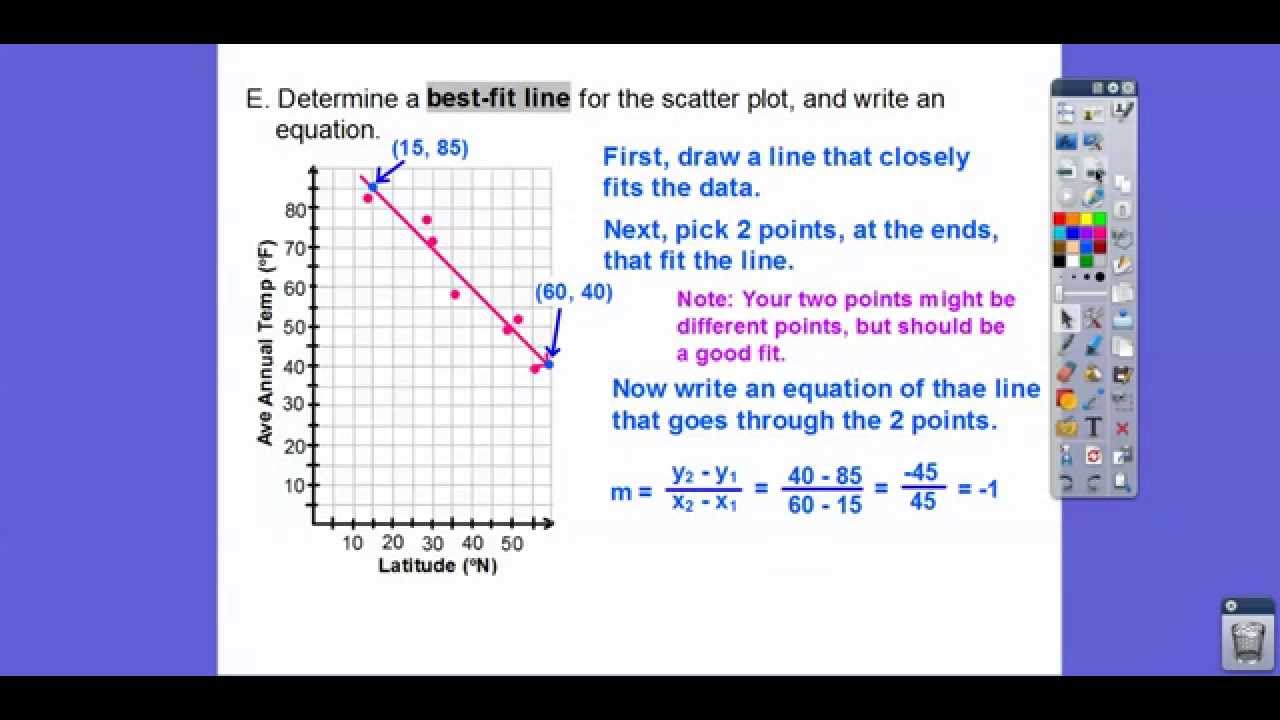
Photo Credit by: bing.com / scatter trend lines plots